Featured peer-reviewed article: Removal of extra sequences with I-Scel in combination with CRISPR/Cas9 technique for precise gene editing in Drosophila
The CRISPR/Cas9 system has recently emerged as a powerful tool for functional genomic studies and has been adopted for many organisms, including Drosophila. Previously, an efficient two-step strategy was developed to engineer the fly genome by combining CRISPR/Cas9 with recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE). This strategy allows the introduction of designed mutations into a gene of interest in vivo.
However, the loxP or frt site remains in the edited locus. Here, we propose a modification of this approach for rapid and efficient seamless genome editing with CRISPR/Cas9 and site-specific recombinase-mediated integration (SSRMI) combined with recombination between homologous sequences induced by the rare-cutting endonuclease I-SceI. The induced homological recombination leads to the removal of the remaining extraneous sequences from the target locus.
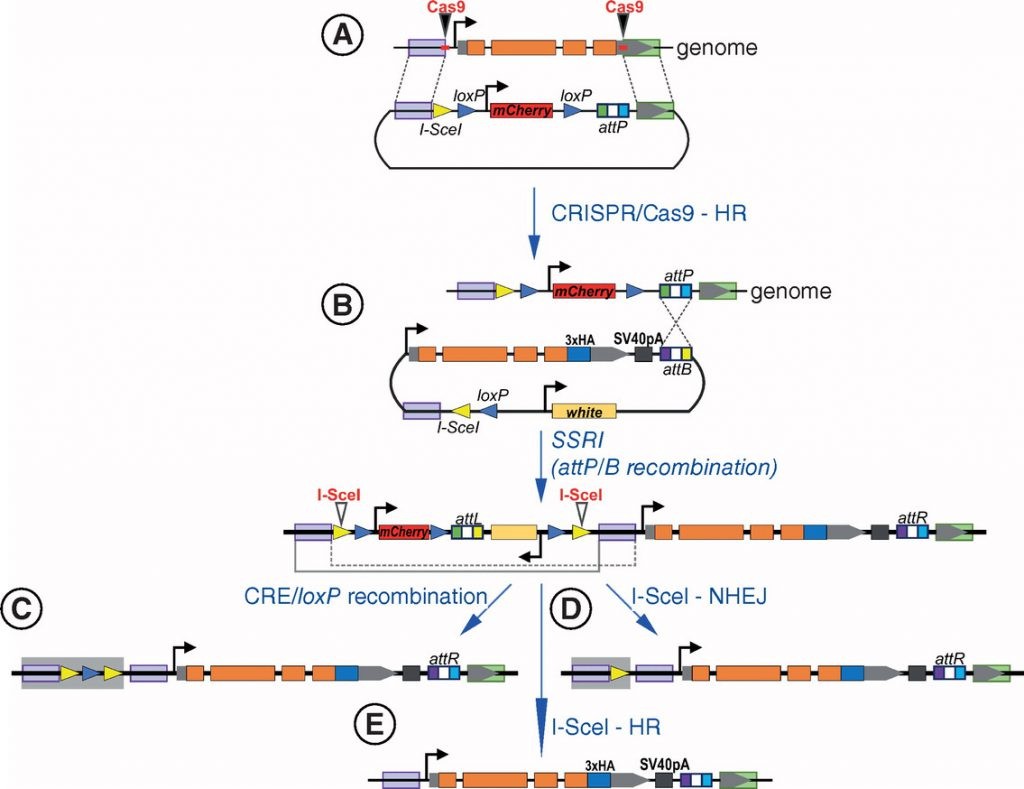
Scheme of gene editing using I-Scel endonuclease in combination with CRISPR/Cas9 and site-specific recombinase-mediated integration techniques.