Those magnificent researchers and their micromachines
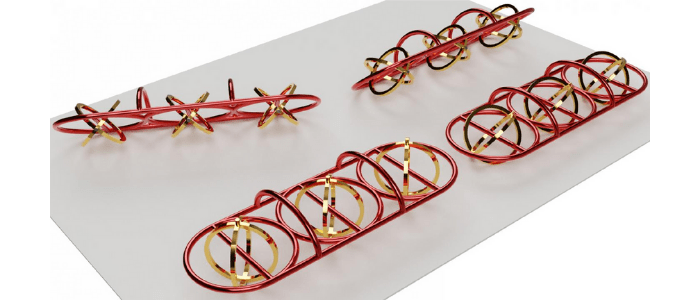
A delicate method of micro-3D printing may have unlocked a new tool in the advancement of drug delivery: ‘micromachines’. A research team at ETH Zurich (Switzerland) has found a way to craft minuscule devices composed of plastic and metal components. The ‘micromachines’ could have a huge impact in the field of drug delivery, allowing clinicians to load the machines with an active substance and deliver it to the target site before releasing it, increasing efficacy and reducing off-target effects. To direct micromachines within the body, magnetic waves are typically used to influence magnetic metal parts. However, metals have limits as...
To view this content, please register now for access
Join our member community for FREE to access a collection of journal and online-only features, including:
- Exclusive access to educational videos, eBooks and insights into top BioTechniques journal articles
- The latest news and journal updates delivered straight to your inbox when you want it
- Personalized recommendations for the latest member-exclusive podcasts, interviews and expert opinions
- Priority registration to webinars, panel discussions and events
- Access to competitions and journal publication discounts, including 10% off open access fees when you sign up today!