Augmented reality and the life sciences

Augmented reality (AR) use in medicine is not just science fiction. Scientists are now utilizing AR for the 3D visualization of DNA test results, organs and more.

Joseph Mikhail is the CRO of Meta (CA, USA), specialists in AR. Joe has successfully driven corporate incubation, technology spinouts and corporate venture capital programs, as well as founding and directing several software startups. He joined Meta from Lenovo (NC, USA), where he identified ground-breaking technologies and established strategic equity investments as the Director of Worldwide Open Innovation.
Please can you define AR for us?
AR is the future of computing, truly. It transcends traditional computing with 2D monitors, mouse and keyboard – and takes us into spatial computing, with 3D holograms and more natural interactions. It’s a whole new way of interacting with digital content in the context of the real world.
Although there are several forms of AR such as mobile and smart glasses, the most advanced and powerful is immersive AR, which is defined as photorealistic, high resolution, life-size holograms wrapped in a natural interaction paradigm using direct hand manipulation and voice commands. Immersive AR has immense potential to change how we communicate, collaborate and create… enhancing our human interaction in the process.
How can AR be used in medicine, medical simulation and training?
Healthcare is one of the primary verticals in AR with the most to gain. In healthcare education, medical schools are starting to train a new generation of healthcare professionals using interactive 3D anatomical models – reducing the need for cadavers and significantly improving training and comprehension.
With immersive 3D medical imaging, AR can assist with everything from diagnosis, to patient communication, to collaborative pre-operative planning, to the surgery itself, where 3D MRI/CT scan is overlaid onto the patient. The benefits of 3D medical imaging go well beyond providing high financial value – they represent the future of care-giving.
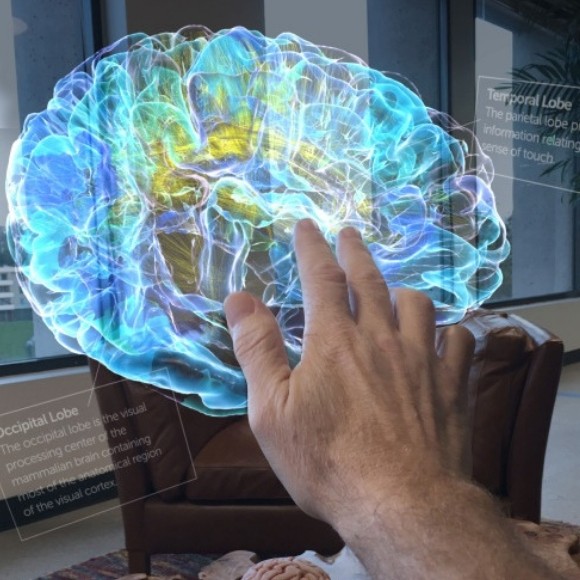
The Meta 2 is ideally suited for medical and scientific applications, because its 2.5k resolution allows you to see the smallest details and interactive hand gestures make manipulation and resizing much more intuitive.
How can AR benefit scientific research?
Given that our cognitive and visual systems are 3D by nature, an intuitive 3D visualization and computational tool is more than an advancement – it’s the natural evolution of research spanning 3D genetic analysis to 3D data visualization. Whenever we distill an originally 3D object into a 2D medium, our cognitive system must work hard at deciphering the information. Applying spatial computing to visualize large data sets and analyze test results of 3D objects frees us to perform scientific research more efficiently.
How can lab-based scientists take advantage of AR?
Immersive AR opens up a world of possibilities across all fields of science. Some customers are exploring 3D visualization of DNA test results, while others are adding more dimensions to their analytics through 3D data visualization. Additionally, using AR glasses with natural interaction, like our Meta 2, provides a high-resolution, hands-free experience that allows for detail analysis with data overlay suitable for clean-room use cases. I encourage lab scientists to explore immersive AR for themselves, and imagine what is possible in their day-to-day work.
Where is AR headed in the future in this field?
We’ll start to see diagnostics taking place in the context of real life, which is tremendously exciting. Since the high-end computer vision system behind immersive AR is scanning the world around you, when you apply object recognition on top of this computer vision system, it enables powerful visual search use cases.
For example, you may simply look at a test subject like a blood or fluid sample and immediately view metadata – perhaps identifying the sample’s structure and properties – and thus draw conclusions and flag anomalies more efficiently. This type of computer-based testing may improve quality and accelerate the testing process.
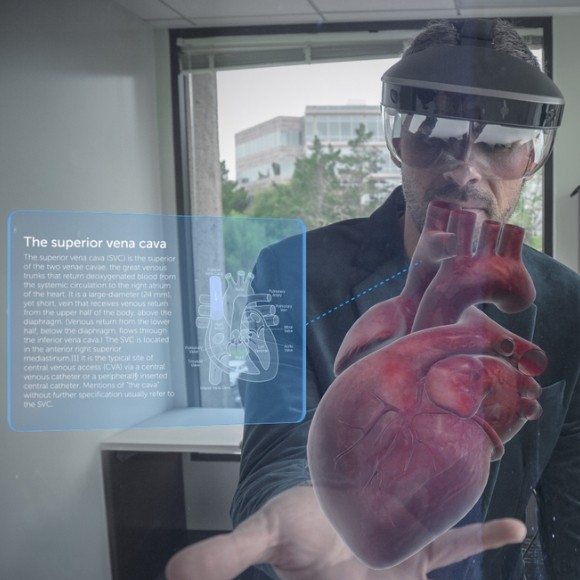

In the medical field, augmented reality applications developed using the Meta 2 can assist with everything from diagnosis, to patient communication, to collaborative pre-operative planning, and even during surgery.
Is there any other important information you would like to share that’s relevant to the research lab professional?
AR is changing every aspect of our professional and personal lives. Just think what it would be like if you could wear a powerful spatial computer like a pair of Oakley glasses – a computer that allows you to interact directly and naturally with the digital world. It would redefine your work in ways that you may not even imagine yet!
We at Meta are passionate about bringing AR technology to as many domains as possible, especially in fields that advance humanity and improve our quality of life. Healthcare and life sciences are primary beneficiaries of this technology transformation, and we are excited and committed to delivering solutions here.