SARS-CoV-2 detected in nasopharyngeal swabs by biosensor
Biosensors are being used as a tool for detecting the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in patients and diagnosing COVID-19. Early and rapid detection of the disease will help manage the outbreak by curbing the spread of the virus.
Now, researchers from institutions across Korea, including the Korea Research Institute of Chemical technology (Daejeon, Republic of Korea) and Korea Basic Science Institute (Cheongju, Republic of Korea) have developed a transistor-based biosensor that can detect the presence of the COVID-19 causing virus, SARS-CoV-2. The test is conducted via a nasopharyngeal swab from patients and is so rapid it can detect the virus in less than a minute.
The current test for COVID-19 as it stands is a PCR test, which requires a multiple step process just for sample preparation, let alone carrying out the full test. To find a faster method of testing that didn’t require such complicated methods for sample preparation the team, led by Edmond Changkyun Park and Seung Il Kim (Korea Basic Science Institute) developed a test that can detect the virus directly from the swab taken from patients, once placed in a test tube with buffer solution.
Sign up to The Nanomed Zone for free
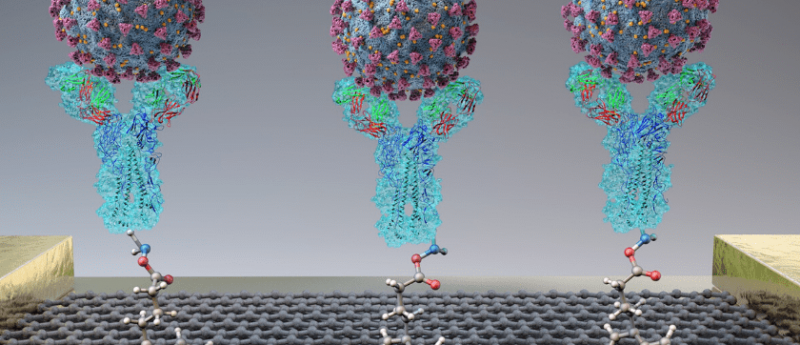
The biosensor was developed from a field-effect transistor made up of nanosheets of graphene, creating a highly conductive surface, which was then coated with a specific antibody against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
They tested the performance of the sensor in experiments involving antigen protein, cultured virus and then specimens from the nasopharyngeal swabs of COVID-19 patients. When purified spike proteins or cultured SARS-CoV-2 viruses were added to the sensor, a change in electrical current was triggered by the binding of the antibodies. The sensor, via this change in electrical current across the graphene sheets could successfully detect the difference between binding of antibodies in patient samples with COVID-19 compared to healthy controls.
This highly sensitive immunological diagnostic test, with the added advantage of not needing pre-treatment sample preparation or labelling could be a very promising biosensor for SARS-CoV-2.
For more free COVID-19 related content please visit our dedicated COVID-19 Hub on Infectious Diseases Hub here.
For more related news from The Nanomed Zone be sure to sign up here.