Single-cell and spatial multiomics identifies Alzheimer’s disease markers
The pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease is incompletely understood. Powerful tools such as single-cell and spatial solutions are important to improve our understanding of disease development and progression. This Application Note uses a multiomics approach to resolve the relationship between progressive changes in cell-type specific differential gene expression and plaque burden in an Alzheimer’s mouse model.
This Application Note highlights:
- The relationship between progressive changes in cell-type specific differential gene expression and plaque burden in an Alzheimer’s-like mouse model
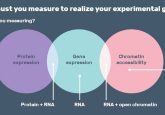
- Differences in gene expression and chromatin accessibility of well-known Alzheimer’s markers between transgenic and wild-type mice in concordance with plaque burden
- The spatial organization of these changes across anatomical brain regions
And much more!
This content was provided by 10x Genomics